티스토리 뷰
DFS는 스택, BFS는 큐
프로그래머스
코드 중심의 개발자 채용. 스택 기반의 포지션 매칭. 프로그래머스의 개발자 맞춤형 프로필을 등록하고, 나와 기술 궁합이 잘 맞는 기업들을 매칭 받으세요.
programmers.co.kr
해당 문제를 보면 int[][] computers 이차원 배열을 파라미터로 주는데, 전형적인 인접행렬 형태다!
가장 기본적인 DFS BFS 문제인것 같아 기억이 새록새록 난다
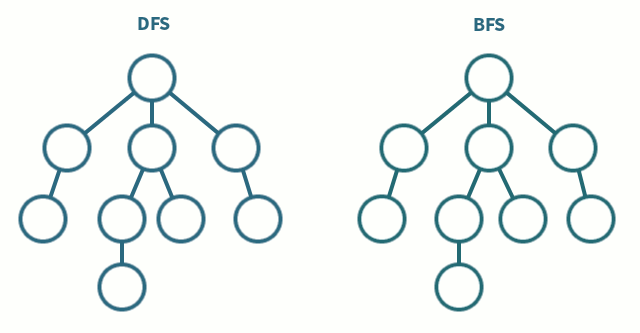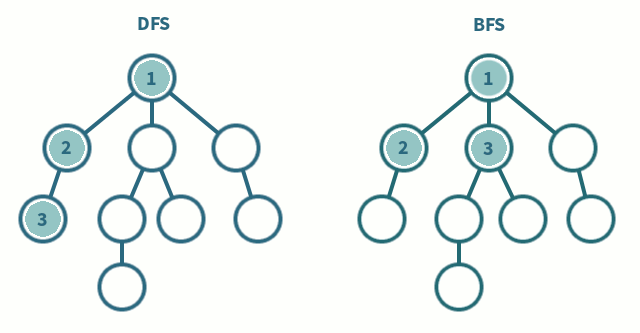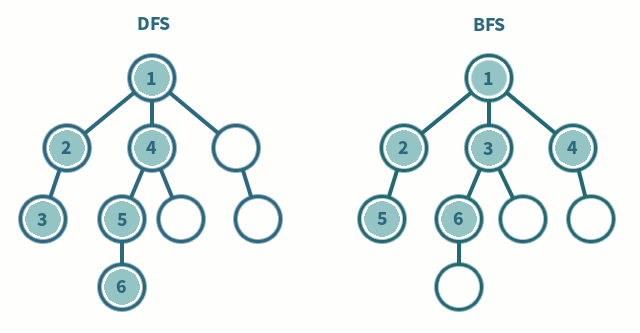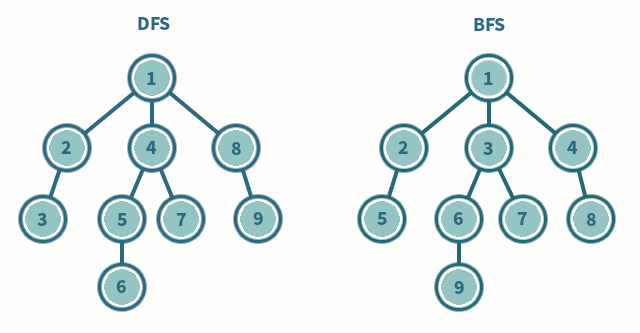
* 인접행렬 사용 시 시간복잡도는 O(V^2)
(V: 정점의 개수)
# DFS
(1) 재귀함수를 통한 DFS
- 재귀함수 자체가 내부적으로 스택을 이용하는 것이다. (메소드 호출 시 스택 생성)
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int solution(int n, int[][] computers) {
int cnt = 0;
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(!visited[i]) {
dfs(computers, visited, i);
cnt++;
}
}
return cnt;
}
private void dfs(int[][] computers, boolean[] visited, int v) {
visited[v] = true;
for(int i = 0; i < computers.length; i++) {
if(computers[v][i] == 1 && !visited[i]) {
dfs(computers, visited, i);
}
}
}
}
(2) 함수 호출을 통한 DFS
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int solution(int n, int[][] computers) {
int cnt = 0;
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(!visited[i]) {
dfs(computers, visited, i);
cnt++;
}
}
return cnt;
}
private void dfs(int[][] computers, boolean[] visited, int v) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
visited[v] = true;
stack.push(v);
while(!stack.isEmpty()) {
Integer w = stack.peek();
visited[w] = true;
boolean hasAdjNode = false; // 방문하지 않은 인접 노드가 있는지?
for(int i = 0; i < computers.length; i++) {
if(computers[w][i] == 1 && !visited[i]) {
visited[i] = true;
hasAdjNode = true;
stack.push(i);
break;
}
}
if(!hasAdjNode) {
stack.pop();
}
}
}
}
# 장점
구현이 비교적 간단하고, 깊은 단계에 있는 해를 더 빨리 찾을 수 있음
# 단점
최단 경로 탐색을 보장할 수 없고, 해가 없는 경로에 깊이 빠진다면 시간만 낭비할 수 있음.
# BFS
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int solution(int n, int[][] computers) {
int cnt = 0;
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(!visited[i]) {
bfs(computers, visited, i);
cnt++;
}
}
return cnt;
}
private void bfs(int[][] computers, boolean[] visited, int v) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
visited[v] = true;
queue.add(v);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
Integer w = queue.poll();
for(int i = 0; i < computers.length; i++) {
if(computers[w][i] == 1 && !visited[i]) {
visited[i] = true;
queue.add(i);
}
}
}
}
}
# 장점
BFS는 최단 경로를 보장할 수 있다.
# 단점
다음에 방문해야할 정점들을 큐에 미리 담아놔야 하기 때문에 저장공간을 DFS보다 많이 사용한다.
근데 이게 왜 레벨 3에 배정된건지 의문이다. ?? 응용도 아니고 완전 기본 DFS BFS 문제인데
아무튼 알고리즘 공부는 꾸준히 안하면 진짜 다 까먹어버리는 것 같다..
오늘부터 다시 1일 1솔브 프로젝트를 가동해야겠다!! 빠샤버려
'알고리즘 > BFS & DFS & 백트래킹' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 프로그래머스 | 가장 먼 노드 - java (0) | 2022.08.24 |
|---|---|
| 프로그래머스 | 여행 경로 - java (0) | 2022.08.22 |
| [JAVA] # 14052 연구소 (0) | 2021.09.19 |
| [JAVA] # 13460 구슬 탈출 2 (0) | 2021.09.18 |
| [JAVA] # 11725 트리의 부모 찾기 (0) | 2021.09.15 |
댓글
